family trustis a trust agreement between family members for the purpose of managing, operating, and passing on property. This is used especially in the aging of the population, as a means of preparing for the event that a person becomes unable to manage his or her own property due to dementia or illness, or to ensure the smooth succession of property in the event of inheritance.
This article provides an overview of "family trusts," how they work, and how to utilize them.
People who should read this article
People who want to prepare for the inheritance of owner-occupied homes.
I've heard of family trusts, but what are they? What is it?
People who want to leave the management of their homes or apartments they rent to others to their children.
Anyone looking for a way to facilitate the inheritance of real estate.
What is a Trust Agreement?
What is a Trust?The consignor.That trusted person or entity(Trustee) to theThe trustee transfers money, land, and other property to the trustee, who then transfers the property in accordance with the trust purposes established by the trustee.For BeneficiariesA system for managing and administering that property (trust assets).
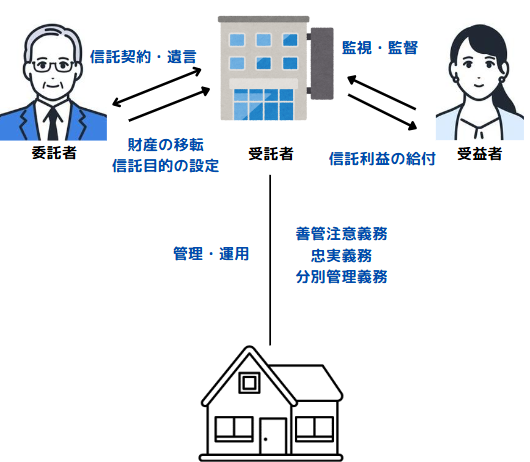
In the diagram above, the trustee (father) transfers property to the trustee (e.g., trust bank) by contract or will and establishes a trust agreement. The trustee then provides benefits (such as rent) to the beneficiary (daughter) according to that contract.
Type of trust agreement
commercial trust
The trust bank or trust company is entrusted with the property by the owner of the property, the trustee, and manages and takes over the property as trustee. At this time, the trust bank or trust company receives trust fees. This commercial trust is regulated by the Trust Act and the Trust Business Act.
Examples of Commercial Trusts
- Education Fund Giving Trust
- Marriage and Childcare Gift Trust
- Specific Disability Dependent Trust
- Guardianship Support Trust
Family Trust (Civil Trust)
A trust in which the trustee assumes the management of the trustor's property for non-profit purposes is called a civil trust. Among civil trusts, the act of entrusting property to a trusted family member is generally referred to as a "family trust.
Family trusts (civil trusts) are subject to the Trust Act, but not the Trust Business Act.
A family trust works as follows.
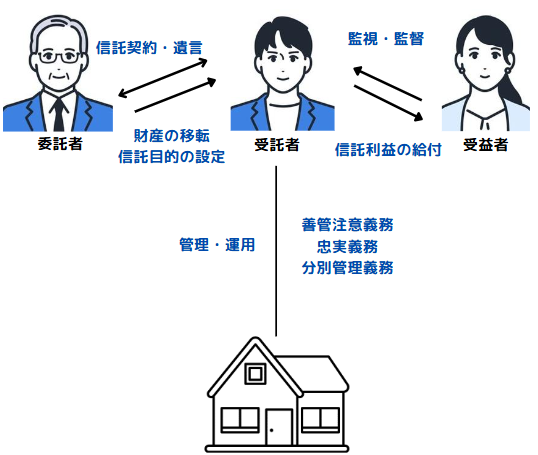
- consignorTrusts: a person (usually a parent or grandparent) trusts another family member (usually a child or grandchild) with the right to manage his or her property.
- trustee: A person who manages the property. In a family trust, a trusted family member (e.g., a child) is usually designated as trustee to manage and administer the trustee's property.
- beneficiaryBeneficiary: The person who receives the benefit from the estate. The trustee often makes himself/herself the beneficiary, but in some cases, another family member (e.g., spouse or children) can be the beneficiary.
The main features and benefits of family trusts are as follows
- Continuity of property managementThe trustee can continue to properly manage the property even if the trustee loses the capacity to make decisions due to dementia or illness.
- Facilitation of legacy successionThe trust agreement can clarify to whom and how the property will be passed on, making it easier to avoid wills and inheritance problems.
- Flexible operations: Since trust agreements can be set up individually, they allow for flexible management according to the family's situation and wishes.
However,Since family trusts require specialized knowledge, it is recommended to consult a lawyer, tax accountant, administrative scrivener, or other specialist to conclude an appropriate trust agreement.In addition, trust assets are subject to inheritance taxes, so tax considerations must be taken into account.
Examples of Family Trusts
Since some aspects of family trusts are difficult to understand, we will introduce some examples of actual use.
Case (1) Self-benefit trust
Mr. A, who is elderly, manages a rental apartment and wanted his eldest son to manage the apartment in case he becomes incapable of making decisions in the future. He consulted an inheritance diagnostician through an acquaintance, learned about the family trust system, and was referred to an administrative scrivener, with whom he concluded a family trust agreement.
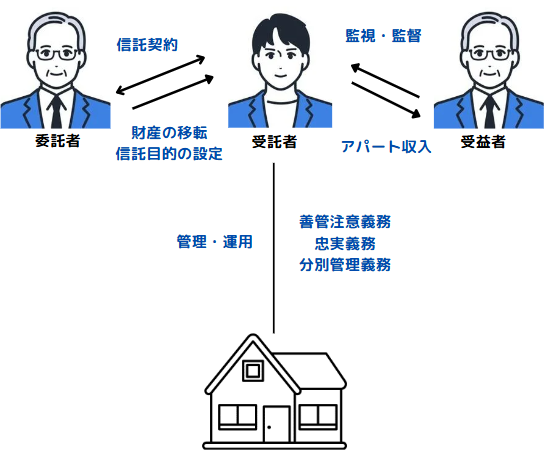
- A rental apartment owned by Mr. A (trustor) is placed in trust for his eldest son (trustee). The beneficiary is Mr. A himself. The name of the apartment is transferred from Ms. A to her eldest son, and the eldest son manages and operates the apartment, but Ms. A continues to receive the rental income from the apartment.
- The eldest son will continue to manage and operate the apartment after Mr. A (trustee) develops dementia. The eldest son may dispose of the rental apartment for his father's living expenses and nursing care expenses, depending on the terms of the trust agreement.
Case (2) Continuous beneficiary trust
Mr. B wanted to inherit the apartment and its land, which he inherited from his ancestors, by his own blood. On the other hand, Mr. B has no children, and although there is no problem with his wife inheriting the property after his death, his wife's brothers and sisters will inherit the property after his wife's death, which is not acceptable.
So after my death, I would like my brother's children (nephews) to inherit this apartment and land.
Mr. B used a family trust to realize his wishes.
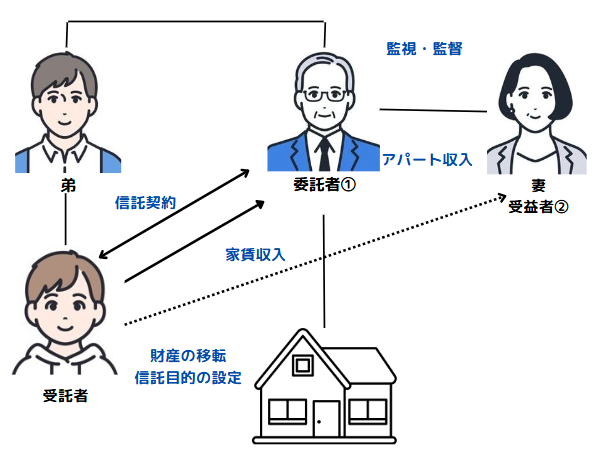
- Mr. B (the trustee) places the apartment he owns in trust for his younger brother's child (nephew), whom he trusts, in preparation for future loss of judgment and in case of inheritance after his death.
- The beneficiary is assumed to be Mr. B himself.
- The title to the apartment is transferred from Mr. B to the trustee (nephew), but Mr. B continues to receive the rental income.
- After Mr. B's death, his wife is the next beneficiary to receive rental income.
- Upon the death of Mr. B's wife, the trust is completed and the nephew inherits the apartment.
summary
How was it?
Family trusts are still unfamiliar today, but they are a mechanism for managing and operating property within the family, and are increasingly in demand as a way to manage property and pass on legacies as we enter a super-aging society. The trustee entrusts his or her property to a trusted family member (trustee), who manages and operates the property in accordance with the designated purpose, thereby ensuring that the trustee's intentions are protected for a long period of time.
- Flexibility in property managementFamily trust: In a family trust, the trustee is free to set the method of management and distribution of property, and the trustee manages the property accordingly. This allows designated family members to properly manage the property even if the trustee loses the ability to make decisions due to dementia or other reasons.
- inheritance measuresFamily trusts are also used as a means of avoiding problems in the event of inheritance. By clarifying in advance how property will be distributed in a trust agreement, disputes among heirs can be prevented.
- Differences from Adult GuardianshipFamily trusts differ from adult guardianship systems in that the will and intentions of the trustee are respected, allowing for more flexible management. Unlike the adult guardianship system, which requires court supervision, family trusts allow for voluntary management based on the trust agreement.
- Tax Considerations: Family trusts also have tax implications, so proper tax planning is required. Expert advice is important because the burden of inheritance and gift taxes varies depending on the form of trust and the type of property.
Family trusts are attracting attention as an effective means of smoothly managing assets and preparing for inheritance and nursing care. However, they can cause problems if not properly designed, so the support of a trusted professional is essential.




Comments